Asian Games
 Asian Games logo |
|
| Motto | Ever Onward |
|---|---|
| First Event | 1951 Asian Games in New Delhi, India |
| Occur every | four years |
| Last Event | 2006 in Doha, Qatar |
| Purpose | Multi sport event for nations on the Asian continent |
The Asian Games, officially known as Asiad, is a multi-sport event held every four years among athletes from all over the Asia. The Games are regulated by Asian Games Federation (AGF) since the first Games in New Delhi, India until 1978 Games and commenced by Olympic Council of Asia (OCA) since 1982 after the dissolved of Asian Games Federation.[1] The Games are recognised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) and are described as the second largest multi-sport event after the Olympic Games.[2][3]
Thailand has hosted four Asian Games, more than any other nation, after twice secured the Games from the crisis. In the history, only nine nations have already hosted at least one Asian Games. 46 nations already participated in the Games, this include Israel, which expelled being part of of the Games since their last participation in 1974.
Contents |
History
Prior formation
Before Asian Games held, that is a game known as Far Eastern Games that formed in 1912 from Empire of Japan, the Philippine Islands and China. The first games were held in Manila in 1913 until 1934 for ten editions. However, due to the second Sino-Japanese War in 1934, and insist to include Manchu Empire as part of the Games nation, China announced their withdrawal from the Games. The Games scheduled for 1938 was cancelled and it is discontinued afterwards. That is another games were held in New Delhi, India in 1934, known as West Asian Games with participation from India, Ceylon, Afghanistan and Pakistan. The Games was scheduled for another edition in 1938, but was cancelled due to World War II.[4]
Formation
After World War II, a number of Asian countries became independent. Many of the new independent Asian countries wanted to use a new type of competition where Asian dominance should not be shown by violence and should be strengthened by mutual understanding. During the 1948 Summer Olympics in London, that is a conversation of sportsman from China and Philippines to restore the Far Eastern Games, however Indian International Olympic Committee representative Guru Dutt Sondhi thinks that the restoration of the Games is not enough to shown the spirit of unity and level of the Asian sports, proposed to sports leaders of the idea of having discussions about holding one new competition—Asian Games. They agreed to form the Asian Athletic Federation. A preparatory committee was set up to draft the charter for the Asian amateur athletic federation. On February 13, 1949, the Asian athletic federation was formally formed in New Delhi and used the name Asian Games Federation, with New Delhi announced as the first host city of the Asian Games which schedule to host in 1950.[4][5]
The planned first Games was delayed to 1951 due to the preparation problems. However, it was successfully organised from March 4–11, 1951 with 489 athletes from 11 countries took part in the Games. The Games growth from one to another edition. In 1958, it was officially announced that "Ever Onward" as the official slogan of the Games.[6]
Crisis, reorganisation
Start 1962, the Games were hit by several crises. The host country Indonesia, refused the participation of Israel and Republic of China due to the political and religious issue. As a result, IOC remove the sponsorship of the Games and terminated Indonesia as one of the IOC members,[7] this also done by the Asian Football Confederation (AFC),[8] International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF) and International Weightlifting Federation (IWF), with the removal recognition of the Games.[9][10]
In 1962, the Federation had a disagreement over the inclusion of Republic of China and Israel. Asian Games host Indonesia opposed the participation of Republic of China (due to the existence of People's Republic of China) and Israel. In 1970, South Korea dropped its plan to host the games due to security threats from North Korea, forcing previous host Thailand to administer the games in Bangkok using the funds of South Korea. In 1973, the Federation had another disagreement after U.S. and other countries formally recognized the People's Republic of China and Arab nations' opposition to Israel. In 1977, Pakistan dropped its plan to host the games due to conflicts with Bangladesh and India. Thailand offered to help and the games were held in Bangkok.
The Asian NOCs decided to revise the constitution of the Asian Games Federation. A new association, named Olympic Council of Asia, was created in November 1981. India was already scheduled to host the 1982 Games and OCA decided not to drop the old AGF timetable. OCA formally supervised the games starting from the 1986 Asian Games in South Korea.
In the succeeding games, Taiwan (Republic of China) was readmitted but OCA decided to follow the standards of the IOC for Taiwan to use the name Chinese Taipei. The OCA also agreed to permanently exclude Israel as its member and requested that the country join European competitions.
Expansion
In the 1994 Asian Games, despite opposition from other nations, OCA admitted the former Soviet republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgystan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, and Tajikistan.
Future changes
Future changes including shrink the competition down to just 35 sports, start with 2014 in Incheon, South Korea. 2014 also see the Games last hosted in even year, as Olympic Council of Asia pushed the subsequent Games to just one year ahead of Olympic Games, this mean the 18th Asian Games which originated in 2018 will push to 2019.
Participation
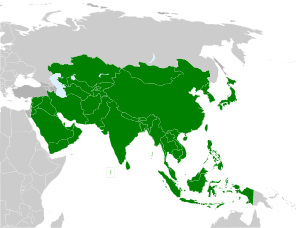
All 45 members affiliate to the Olympic Council of Asia (OCA) are eligible to take part in the Games. In history, the Games had been took part by 46 National Olympic Committees. Israel was excluded from the Games since 1976, cited it is due to security reasons,[11] although they requested for participation in 1982 Games, but it is rejected by the organisers due to incident in 1972 Summer Olympics,[12] now they are a member of European Olympic Committees (EOC).
Due to political status, Taiwan is participate under the flag of Chinese Taipei since 1990. Macau are allow to compete as one of the NOC in Asian Games, despite it is not recognised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) to participate in Olympic Games.
In 2007, president of OCA, Sheikh Ahmad Al-Fahd Al-Sabah rejected the proposal to allow Australia to participate in the Games, like in Football, by stated while Australia will add good value for Asian Games, but it is unfair to the other NOCs in Oceania.[13]
Sports
|
|
|
Medal count
Of the 46 National Olympic Committees participated throughout the history of the Games, 43 nations already won at least a single medal in the competition, leaving three nations: Bhutan, Maldives and Timor-Leste yet to win a single medal. 34 nations already won at least a single gold medal, while Japan and China became the only two nations in history to emerge as overall champions.
List of Asian Games
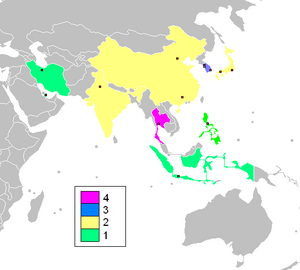
The Olympic Council of Asia usually granted the right to host six or seven years prior to the Games. In the sixteen edition of Asian Games, Bangkok emerged as the most city to host the Games, four times, they are twice rescue the Games, the first one in 1970 which original to be host by South Korea, but declined due to national security crisis, however the main reason was due to financial crisis.[14] Prior to the Games, Japan was asked to host the Games, but declined due to Expo '70.[15] Second time was in 1978, originally to be host by Pakistan, but declined due to financial crisis and political issues.[16] For 2019 and 2023, OCA has asked the bidders to submit the letter of intent altogether before June 30, 2010, while actual bidding document deadline will be at the end of 2010.[17]
| Year | Games | Host | Dates | Nations | Athletes | Sports | Events | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1951 |
|
March 4–11 | 11 | 489 | 6 | 57 | [18] | |
| 1954 |
|
May 1–9 | 19 | 970 | 8 | 76 | [19] | |
| 1958 |
|
May 28–June 1 | 16 | 1,820 | 13 | 97 | [20] | |
| 1962 |
|
August 24–September 4 | 12 | 1,460 | 13 | 88 | [21] | |
| 1966 |
|
December 9–20 | 16 | 1,945 | 14 | 143 | [22] | |
| 1970 |
|
August 24–September 4 | 16 | 2,400 | 13 | 135 | [23] | |
| 1974 |
|
September 1–16 | 19 | 3,010 | 16 | 202 | [24] | |
| 1978 |
|
December 9–20 | 19 | 3,842 | 19 | 201 | [25] | |
| 1982 |
|
November 19–December 4 | 23 | 3,411 | 21 | 147 | [26] | |
| 1986 |
|
September 20–October 5 | 22 | 4,839 | 25 | 270 | [27] | |
| 1990 |
|
September 22–October 7 | 36 | 6,122 | 29 | 310 | [28] | |
| 1994 |
|
October 2–16 | 42 | 6,828 | 34 | 337 | [29] | |
| 1998 |
|
December 6–20 | 41 | 6,554 | 36 | 376 | [30] | |
| 2002 |
|
September 29–October 14 | 44 | 7,711 | 38 | 419 | [31] | |
| 2006 |
|
December 1–15 | 45 | 9,520 | 39 | 424 | [32] | |
| 2010 |
|
November 12–27 | 42 | 476 | ||||
| 2014 |
|
September 19–October 4 | Future event | |||||
| 2019 |
|
TBD (2011) | TBD | Future event | ||||
| 2023 |
|
TBD (2011) | TBD | Future event | ||||
References
- ↑ "OCA History". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Council/History.aspx. Retrieved 2010-08-14.
- ↑ Sportsbizasia.com
- ↑ Sports-city.org
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "亚运会是从什么时候开始举办的,每几年举办一次?". wangchao.org. http://zhidao.wangchao.net.cn/detail_2890838.html. Retrieved 2010-08-14.
- ↑ "亚运会的前世今生:前身远东运动会 中国成绩优异". Sina. 2010-08-04. http://sports.sina.com.cn/o/2010-08-04/04065133499.shtml. Retrieved 2010-08-14.
- ↑ "第3届 1958年东京亚运会". data.sports.163.com. http://data.sports.163.com/match/history/0005000BBQFS.html. Retrieved 2010-08-14.
- ↑ "Track: Asian Games Dropped By Olympics". Daytona Beach. 1962-08-23. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=q3cjAAAAIBAJ&sjid=ZMoEAAAAIBAJ&pg=738,3903294&dq=1962+asian+games&hl=en. Retrieved 2010-08-14.
- ↑ "第4届 1962年雅加达亚运会". data.sports.163.com. http://data.sports.163.com/match/history/0005000BBQFO.html. Retrieved 2010-08-14.
- ↑ "Penalty Dealt to Indonesia". Spokane Daily Chronicles. 1962-09-13. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=kMESAAAAIBAJ&sjid=RvcDAAAAIBAJ&pg=4386,3223549&dq=1962+asian+games+iaaf&hl=en. Retrieved 2010-08-14.
- ↑ "Warning". The Age. 1962-08-30. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=al8RAAAAIBAJ&sjid=jJYDAAAAIBAJ&pg=1306,4815390&dq=1962+asian+games+weightlifting&hl=en. Retrieved 2010-08-14.
- ↑ "Asian Games ban Iarael". St. Petersburg Times. 1976-07-26. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=lR8MAAAAIBAJ&sjid=dl0DAAAAIBAJ&pg=2486,2066961&dq=israel+asian+games&hl=en. Retrieved 2007-07-29.
- ↑ "Israel not invited to Asian Games". Lakeland Ledger. 1982-05-26. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=YJAsAAAAIBAJ&sjid=PvsDAAAAIBAJ&pg=5458,3706701&dq=israel+asian+games&hl=en. Retrieved 2007-07-29.
- ↑ "No place for Australia in Asian Games". The Times of India. 2007-04-17. http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/No-place-for-Australia-in-Asian-Games/articleshow/1918245.cms. Retrieved 2010-07-29.
- ↑ "第六届 1970年曼谷亚运会". Data.sports.163.com. http://data.sports.163.com/match/history/0005000BBQFL.html. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "Thailand’s Sporting Spirit". Pattaya Mail Sports. http://www.pattayamail.com/277/sports.htm#hd4. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "第8届 1978年曼谷亚运会". Data.sports.163.com. http://data.sports.163.com/match/history/0005000BBQFI.html. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "亚奥理事会:亚运会2014年后不在双数年举行". GAGOC. 2010-01-21. http://www.gz2010.cn/10/0121/07/5THLE3ME0078000U.html. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "1st AG New Delhi 1951". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=5. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "2nd AG Manila 1954". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=6. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "3rd AG Tokyo 1958". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=7. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "4th AG Jakarta 1962". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=8. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "5th AG Bangkok 1966". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=9. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "6th Asian Games Bangkok 1970". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=10. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "7th AG Tehran 1974". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=11. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "8th AG Bangkok 1978". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=12. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "9th AG New Delhi 1982". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=13. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "10th AG Seoul 1986". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=14. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "11th AG Beijing 1990". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=15. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "12th AG Hiroshima 1994". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=16. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "13th AG Bangkok 1998". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=17. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "14th AG Busan 2002". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=18. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
- ↑ "15th AG Doha 2006". OCA. http://www.ocasia.org/Game/GameParticular.aspx?GPCode=19. Retrieved 2010-07-22.
External links
|
|||||
|
|||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||